
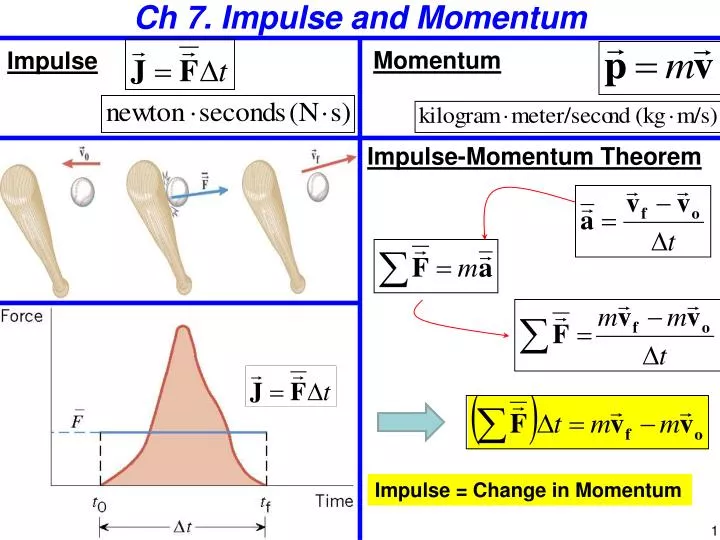
Extra Help – Momentum and Impulse Connection: Ĩ. Extra Help – Momentum and Impulse Connection: ħ. Mechanical Universe – Episode 4 – Inertia: Ĥ.

#Textlab ch 8 momentum license
Ice Bergs/Ocean by Charlton under the CC BY 3.0 license REFERENCESġ. Question: If ocean currents generally move these icebergs at an average of 0.5 m/s what would be its momentum? As coordinators and developers of research and infrastructure projects, we are responsible for large, national resources, including: corpora of spoken languages such as Norwegian dialects and.
#Textlab ch 8 momentum free
Calved from the Ross Ice Shelf in March 2000, B-15 broke up into several pieces in 2000, 20, the largest of which, B-15A, was the world’s largest free floating object at 27 x 122 km with an area of 3,100 km 2 (approximately the size of Luxembourg) with a height averaging 37 m above the water’s surface. At the Text Laboratory we develop technological solutions for text and speech for researchers and students, both at the University of Oslo and nationally. Icebergs have a density of around 900 kg/m 3 and only about 10% of the iceberg can be seen above the surface (90% is below the surface).
What unbalanced force will bring a car weighing 10 000 N from rest to a speed of 108 km/h in a time of 15 s?Ĩ.4.2 The Antarctic Iceberg B-I5A Drygalski Ice Tongue taken by the NASA Aqua satellite under the public domain This force causes this marble to rebound at 2.0 m/s. A marble (3.30 x 10-3 kg) moving at a uniform velocity of 12 m/s experiences a retarding force for 2.0 x 10-3 s. What impulse is necessary to cause this railway car to travel:ġ2. As coordinators and developers of research and infrastructure projects, we are responsible for large, national resources, including: corpora of spoken languages such as Norwegian dialects and American Norwegian heritage language corpora of web texts, literature and student texts databases and word lists for a large selection of languages.As pa. A 4.44 x 103 kg railway car coasts along an east/west track at 8.0 m/s east. What is the amount of time that a force of 4.0 N east must last to produce an impulse of:ġ1. What impulse is produced by a force of 340 N west acting for 5.0 μs?ġ0. What impulse is produced by a force of 21 N east acting for 0.30 s?ĩ. What unbalanced force acts on this kite?Ĩ. A 0.50 kg kite changes its velocity from 12 m/s down to 6.0 m/s up in a time of 1.5 s. If this mass was originally traveling at 10 m/s: (i) What final speed did it reach? (ii) How far did it travel during these 2.0 s?ħ. An unbalanced force of 68 N acts on a 17 kg mass for 2.0 s. (i) What is the acceleration? (ii) What is the magnitude of this unbalanced force?Ħ. An unbalanced force accelerates a 25 kg mass from 12 m/s to 27 m/s in 5.0 s. If the car was initially traveling at 16.5 m/s south, what is the final velocity of this car?ĥ. A 2250 N braking force acts on a 750 kg car for 2.5 s. Course Description: This first term of calculus-based Physics will cover linear and planar motion, Newtons Laws, work and energy, gravitation, momentum. What is the change in velocity of this rock?Ĥ. A 156 N unbalanced force directed east acts on an 18 kg rock for 0.150 s. What unbalanced force would cause a 13.5 kg object to change its speed by 6.50 m/s in 1.30 s?ģ. there are two special types of angular momentum of an object: the spin.

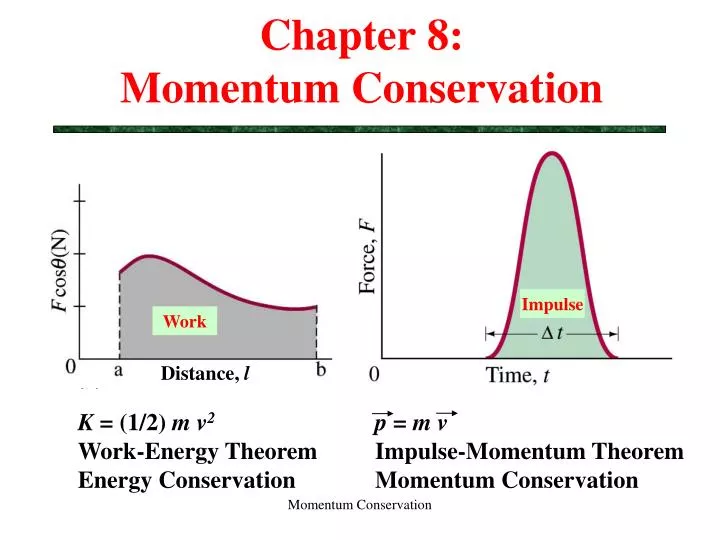
An unbalanced force of 450 N acts on an object for 4.0 s. Mrbly licensed for non-commercial use only / ch 8 bonding general resonance. This integral is telling us to take the probability that the particle is in the interval \(dx\) at \(x\), which is \(ψ^*(x)ψ(x)dx\), multiply this probability by the potential energy at \(x\), and sum (i.e., integrate) over all possible values of \(x\).1.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
